Is MCT Oil the Same as Coconut Oil?

You are probably reading this and already have an idea of what MCT oil is and chances are, you already use coconut oil in your day-to-day life. Both oils have gained a lot of popularity over recent years, but have you ever wondered just how different these oils are, and what they can do for you? This is exactly what we will be investigating today and with any luck, by the end of this blog post you’ll have a better understanding of the difference between MCT and coconut oil.
MCT oil, also known as medium-chain triglyceride is a concentrate of MCT and is derived from a number of different sources. Coconut oil comes from the tropical fruit, coconuts and contains one of the best sources of MCT. There are a few differences, such as MCT oil being known as a dietary supplement and is a form of saturated fat that contain shorter chains of carbon atoms meaning it is easily digested and transformed into energy.
Many who follow the keto diet use MCT oil to help convert ketones in the liver to break down fat rapidly and give the body a boost of energy. The ketogenic diet consists of high fats and low carbohydrates, with MCT oil and coconut oil alike containing high levels of saturated fats and no carbs, both oils are an effective and beneficial addition to the keto diet.
MCTs, are a type of saturated fat and triglyceride consist of a total of three fatty acids and glycerol molecule both of which are made up of carbon atoms, these carbon atoms can vary in length with some MCT oils containing up to 12 carbon atoms in total. The reason it is important to understand these carbon atom chains is the that the smaller chains do not require enzymes or acid to help with breaking the oil down for digestion, instead you’ll find it goes straight to the liver which begins to breakdown fat. There are 4 types of MCT in total, which are the following.
- Caproic acid, containing 6 carbon atoms
- Caprylic acid which contains 8 carbon atoms
- Capric acid which has 10 carbon atoms
- Lauric acid that has 12 carbon atoms
It is thought that the most effective MCT oils are C8 and C10, both of which are best for ketone production and to help aid weight loss.
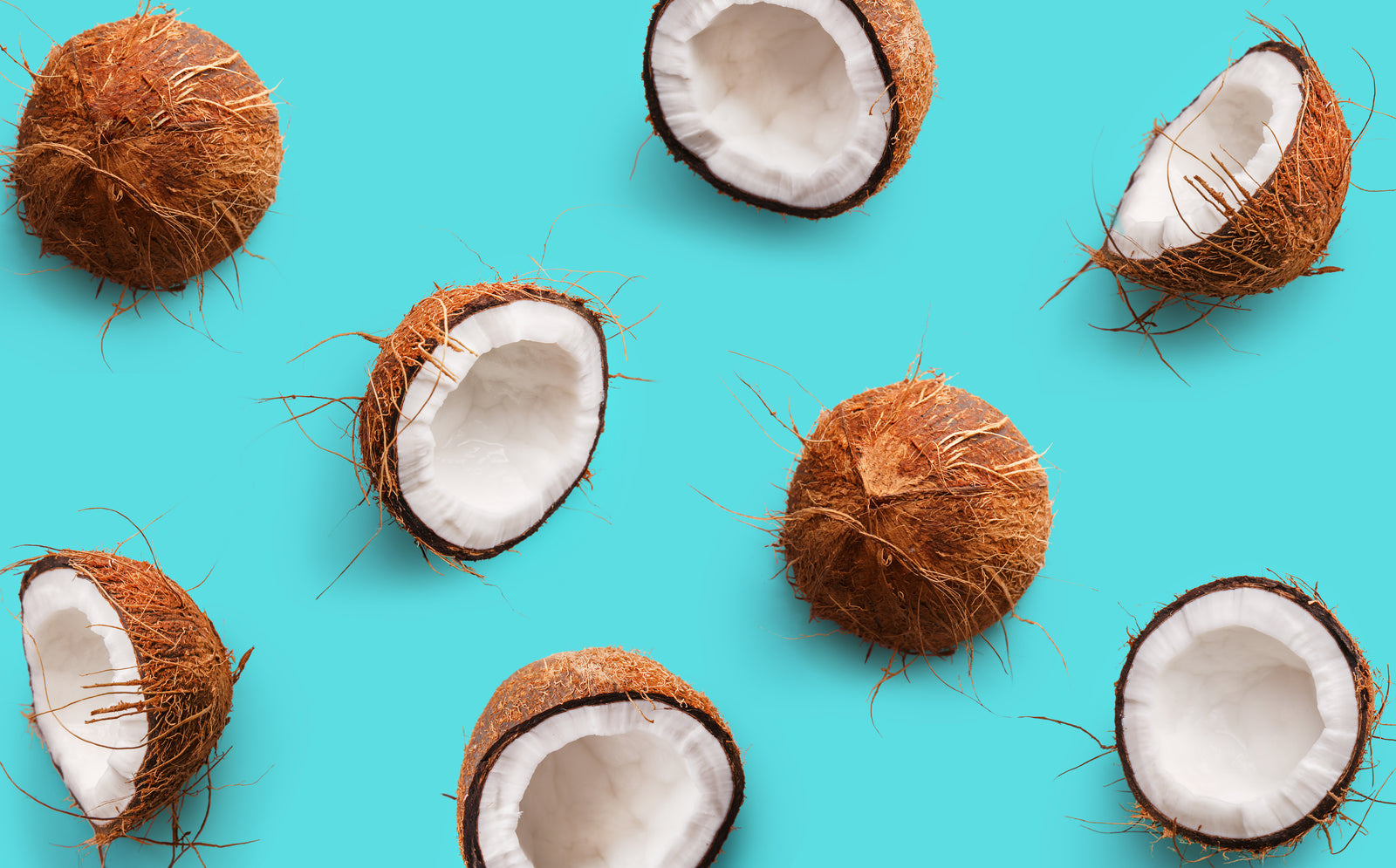
As for coconut oil, this oil is harvested from the dried flesh of the coconut and is known for containing high levels of saturated fats, up to 90% to be exact, 50% of which is MCT compounds.
So, now that I have briefly touched on the differences between MCT oil and coconut oil, I’ll now get stuck in to answering some of your other questions.
Can I substitute coconut oil for MCT oil?
You can, but there really isn’t much point as both MCT oil and coconut oil contain high percentages of saturated fats meaning they can each be used in the keto diet. The only slight difference between MCT and coconut is there scientific backing suggesting that MCT oil has a much more effective at helping you remain feeling fuller for a longer amount of time. Some may suggest that coconut oil has a similar result, however it is in fact the MCT found in coconut oil that helps with feeling full.
Is coconut oil a good substitute for MCT oil?
Yes, coconut oil can be considered a good substitute for MCT oil, as I have already mentioned there is some similarities to both these oils.
What is coconut oil?
- Made from the flesh and kernel of coconuts
- Contains the richest source of MCT making up to over 50% of the compound found in coconut oil
- Contains lauric acid which has a slow absorption and digestion resulting in coconut oil technically being considered not a MCT rich oil, despite the high levels of MCT in its structure
What is MCT oil?
- Contains 100% MCTs making it a concentrated source of MCT oil
- Formulated by using existing oils that are then refined using both raw coconut and palm oil
- MCT oils contain high percentages of caprylic acid between 50-80% and caproic acid rich in 20-50%
What can I substitute for MCT oil?
There are no other substitutes to MCT oil that will be as effective as coconut oil. Admittedly, coconut oil will be unable to deliver the same results but is considered the closest option to choose from. The two main reasons you would find substituting MCT oil for coconut oil will be most effective is in cooking and beauty treatments, such as hair masks and makeup removal.
Another downside to coconut oil compared to MCT is the fact that coconut oil contains extra MCTs in its structure, such as caproic acid and lauric acid, both of which carry very little health benefits. This is why coconut oil is a great alternative, but I wouldn’t suggest making the swap a permanent thing, especially if you are wanting to follow the keto diet effectively.
Is MCT oil bad for your liver?
Yes, it can be if you suffer from uncontrolled diabetes and liver diseases such as cirrhosis. It is best to avoid using MCT oil altogether if you have any of these concerns. This is because MCT oil metabolises in the liver with the rapid absorption and digestion having the opposite results. If you have any of these concerns and are still wanting to introduce MCT oil into your daily routine, I suggest consulting with your doctor first to ensure you are using this powerhouse ingredient properly.
Does MCT oil make you poop?
Yes, it can especially when you first start taking MCT oil. This is because it can draw water from the surrounding areas into your colon which will then soften stools which can often lead to diarrhoea. Therefore, it is important to introduce MCT oil slowly into your routine starting with smaller amounts, such as a teaspoon and work your way up to larger doses once the body has built a tolerance.
There you have it, more information about MCT oil and coconut oil. Don’t forget, if you have any further questions, come, and find us on Instagram.